https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1854
1854번: K번째 최단경로 찾기
첫째 줄에 n, m, k가 주어진다. (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2000000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100) n과 m은 각각 김 조교가 여행을 고려하고 있는 도시들의 개수와, 도시 간에 존재하는 도로의 수이다. 이어지는 m개의 줄에
www.acmicpc.net
1.문제설명

1번 노드에서 출발하여 다른 모든 노드까지의 K번째 최단 거리를 찾는 문제이다.
일반적으로
한 노드에서 다른 모든 노드까지의 최단 거리를 구할 때 다익스트라 알고리즘을 이용한다.
이 문제도 다익스트라 알고리즘을 응용하면 K번째 최단거리를 구할 수 있다.
2.접근방법[알고리즘]
이 문제에서 가장 헷갈리는 점은
기존 최단거리를 구하는 다익스트라 알고리즘과 다르게
방문한 노드를 재방문해도 된다는 점이다.
방문한 노드를 재방문해도 되도록 코드를 구성하면
계속 무한루프에 빠지지 않을까?
이를 해결하기 위해
방문 여부 대신 다른 조건을 추가해주어야 한다.
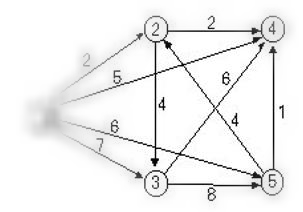
그림에 잘 보면 2->3->5->2가 계속 무한으로 순환할 수 있다.
노드를 방문하는 우선순위큐와 다르게
특정 노드까지 거리를 저장하는 우선순위큐 배열을 따로 두어서
K번째 최단 거리까지 구했다면 더 이상 순환하지 않도록 코드를 구현해야 한다.
3.문제풀이코드 C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m, k;
struct Edge {
int x;
long long val;
bool operator<(const Edge& b) const {
return val > b.val;
}
};
vector<pair<int, int> > graph[1001];
priority_queue<int> Node[1001];
priority_queue<Edge> Q;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
graph[a].push_back({ b,c });
}
Node[1].push(0);
Q.push({ 1,0 });
while (!Q.empty()) {
int x = Q.top().x;
int val = Q.top().val;
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) {
int nx = graph[x][i].first;
int nd = graph[x][i].second + val;
if (Node[nx].size() < k) {
Node[nx].push(nd);
Q.push({ nx,nd });
}
else {
if (Node[nx].top() > nd) {
Node[nx].pop();
Node[nx].push(nd);
Q.push({ nx,nd });
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (Node[i].size() < k) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
else {
cout << Node[i].top() << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
'Algorithm > problem' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2887번 : 행성 터널 - 크루스칼 (0) | 2022.02.18 |
|---|---|
| 백준 1197번 : 최소 스패닝 트리 - Kruskal & Prim Algorithm (0) | 2022.02.18 |
| 백준 1507번 : 궁금한 민호 - 플로이드 활용 C++ (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 백준 1956번 : 운동 - 플로이드와샬 C++ (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 백준 2458번 : 키 순서 - 플로이드 와샬 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.02.17 |