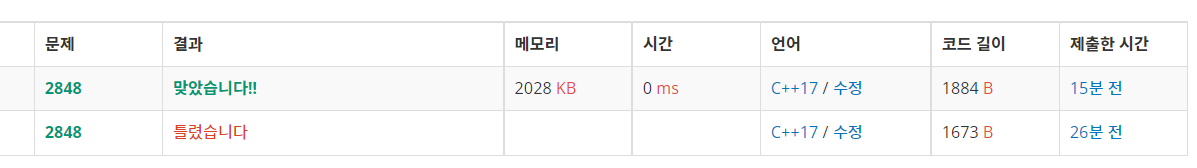
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1199
1199번: 오일러 회로
첫 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000)이 주어진다. 그리고 다음 N개의 줄에 대해 인접행렬의 정보가 주어진다. i+1번째 줄에는 i번 정점에 대한 인접행렬이 주어진다. 두 정점 사이에 간선이 여러
www.acmicpc.net
1.문제 설명
https://m.blog.naver.com/kks227/220800097205
오일러 경로(Eulerian Path), 오일러 회로(Eulerian Circuit) (수정: 2019-08-20)
이번에 소개할 내용은 오일러 경로(Eulerian trail) 및 오일러 회로(Eulerian circuit)입니다. 위상수학,...
blog.naver.com
주어진 입력값을 바탕으로 오일러 회로인지 판별하고
오일러 회로의 경로를 출력하는 문제입니다.
위 블로그에 자세한 설명이 되어있습니다.
2.접근방법[알고리즘]
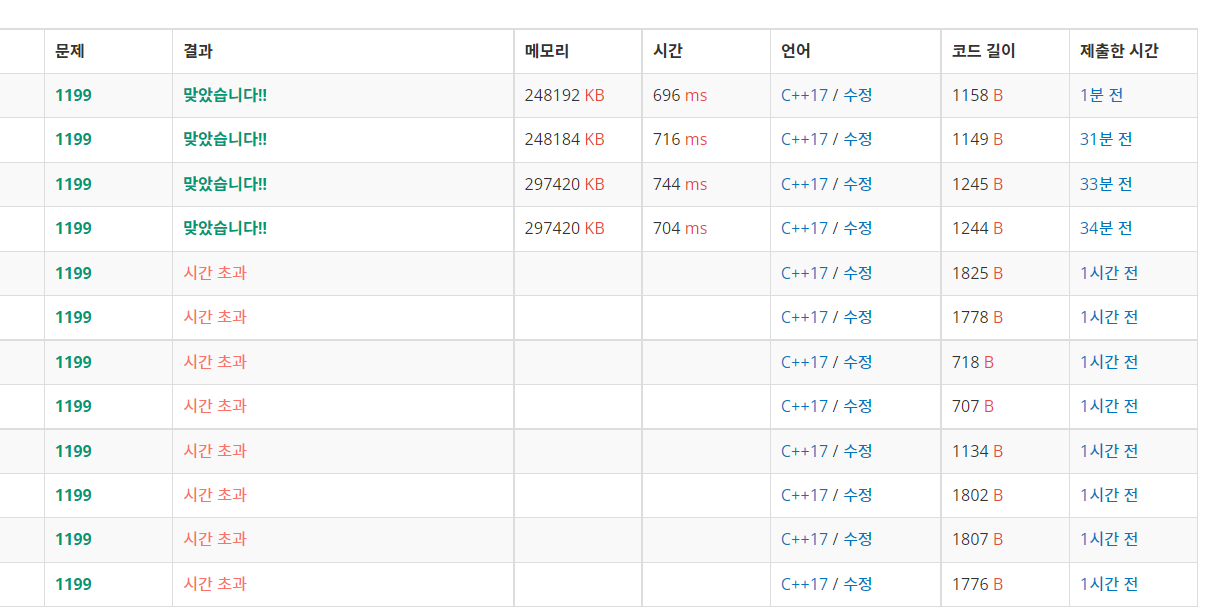
최근 재채점이 된 이후 위 블로그의 풀이가 시간초과가 납니다.
그래서 다른 방법으로 간선 정보를 구현해야합니다.
vector<int> adj[MAX];
vector<pair<int, int> > Edge;
int Edge_cnt[MAX * MAX];
int edge_num;A, B 노드가 있을 때
노드 번호 (A,B)를 Edge 벡터에 저장하고
A와 B 를 이어주는 간선(A,B)에 번호(edge_num)를 주고
A와 B의 간선의 개수를 저장하는 배열(Edge_cnt)을 만듭니다.
이를 이용해 DFS를 돌면서 경로를 출력해주면 됩니다.
3.문제풀이코드 C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX 1001
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> adj[MAX];
vector<pair<int, int> > Edge;
int Edge_cnt[MAX * MAX];
int edge_num;
void DFS(int x) {
while (adj[x].size()) {
int e = adj[x].back();
int u = Edge[e].first;
int v = Edge[e].second;
if (Edge_cnt[e]) {
Edge_cnt[e]--;
if (x == u) {
DFS(v);
}
else {
DFS(u);
}
}
else adj[x].pop_back();
}
cout << x+1 << ' ';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int degree = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int val;
cin >> val;
if (i < j && val >0) {
Edge.push_back({ i,j });
Edge_cnt[edge_num] = val;
adj[i].push_back(edge_num);
adj[j].push_back(edge_num++);
}
degree += val;
}
if ((degree % 2) == 1) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
return 0;
}
}
DFS(0);
return 0;
}
'Algorithm > problem' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 1178번 : 간선 추가 - 오일러 경로 , Union&Find 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.02.28 |
|---|---|
| 백준 16168번 : 퍼레이드 - 오일러 회로 C++ (0) | 2022.02.28 |
| 백준 18111번 : 마인크래프트 C++ 코드 (0) | 2022.02.26 |
| 백준 1948번: 임계경로 - 위상정렬 C++ (0) | 2022.02.26 |
| 백준 2848번 : 알고스팟어 - 위상정렬 C++ 코드 (0) | 2022.02.25 |