https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/4256
4256번: 트리
첫째 줄에 테스트 케이스의 개수 T가 주어진다. 각 테스트 케이스의 첫째 줄에는 노드의 개수 n이 주어진다. (1 ≤ n ≤ 1,000) BT의 모든 노드에는 1부터 n까지 서로 다른 번호가 매겨져 있다. 다음
www.acmicpc.net
1. 문제설명
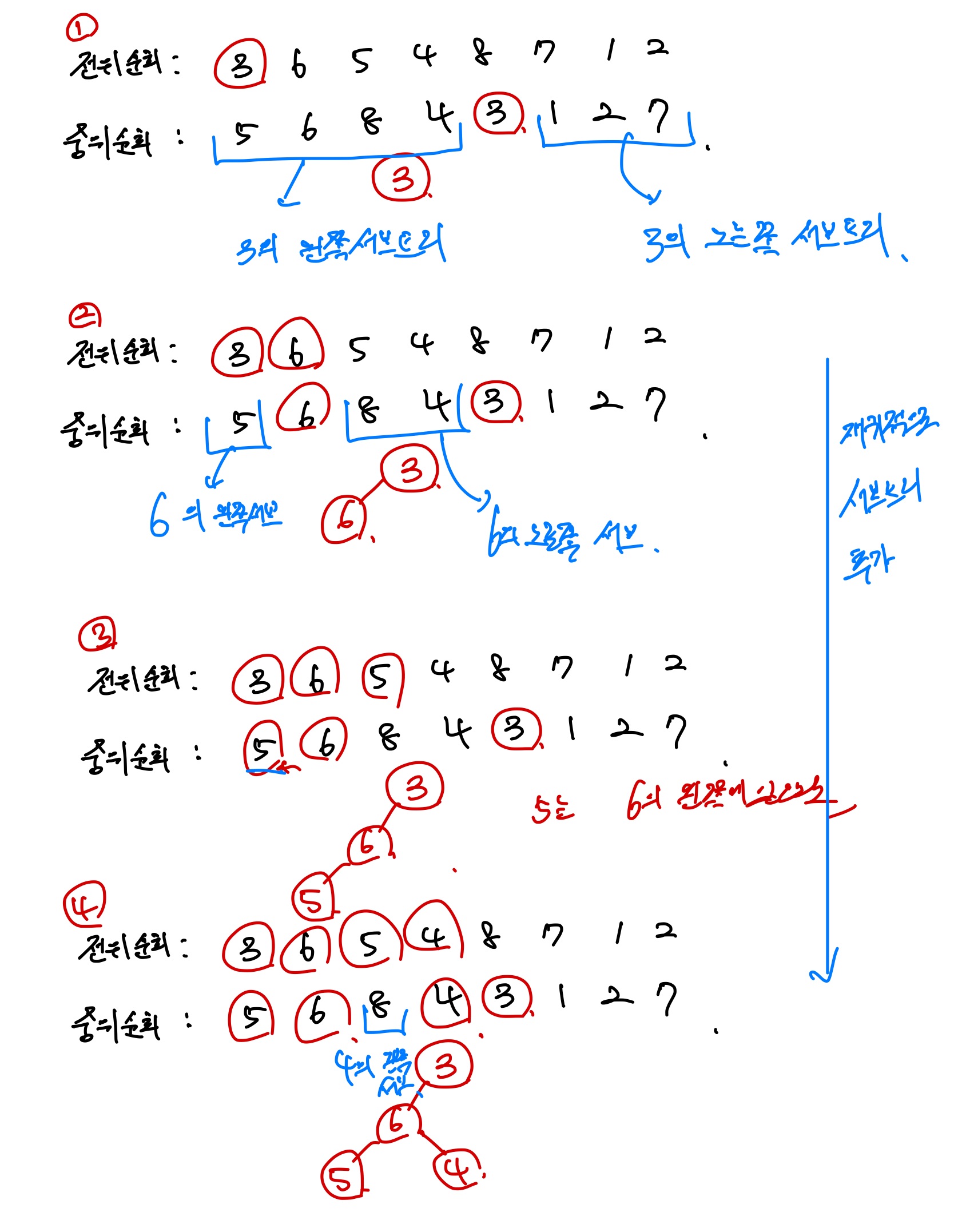
트리의 전위순회 결과와 중위순회 결과를 바탕으로 트리의 구조를 구해낼 수 있고,
이를 후위순회한 결과를 출력하는 문제이다.
전위 순회한 결과 먼저오는 노드가 루트노드임을 알 수 있고,
그 루트노드를 바탕으로 중위순회 결과를 보면
해당 루트노드의 왼쪽 서브트리와 오른쪽 서브트리를 알 수 있다.
이를 재귀적으로 구현하면 트리 구조를 구현할 수 있고,
이를 후위순회하면 정답이 된다.
2. 문제풀이코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,pidx, preOrderRes[1001], inOrderRes[1001], order[1001];
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left = nullptr;
Node* right = nullptr;
Node(int _data, Node* _left, Node* _right): data(_data), left(_left), right(_right){}
};
void postOrder(Node* root){
if(root== nullptr) return;
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
cout << root->data << ' ';
}
void deconstruct(Node* root){
if(root == nullptr) return;
deconstruct(root->left);
deconstruct(root->right);
root = nullptr;
delete root;
}
Node* makeTree(int start, int end){
if(start > end) return nullptr;
Node* newNode = new Node(preOrderRes[pidx++], nullptr, nullptr);
if(start==end) return newNode;
int mid = order[newNode->data];
newNode->left = makeTree(start, mid-1);
newNode->right = makeTree(mid+1, end);
return newNode;
}
void makeTree(Node** root){
pidx = 1;
*root = makeTree(1, n);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
for(int T=0; T<t; T++){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
cin >> preOrderRes[i];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
cin >> inOrderRes[i];
order[inOrderRes[i]] = i;
}
Node *root = nullptr;
makeTree(&root);
postOrder(root);
cout << '\n';
deconstruct(root);
}
return 0;
}'Algorithm > problem' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 15681번 : 트리와 쿼리 - DFS , C++ (0) | 2022.10.02 |
|---|---|
| 백준 1949번 : 우수마을 - 트리 C++ (0) | 2022.10.02 |
| 백준 5639번 : 이진 검색 트리 - 트리 구현 후위 순회 C++ (0) | 2022.10.01 |
| 백준 2250번 : 트리의 높이와 너비 - 트리, C++ (0) | 2022.10.01 |
| 백준 5670번 : 휴대폰 자판 - Trie C++ (0) | 2022.09.28 |
