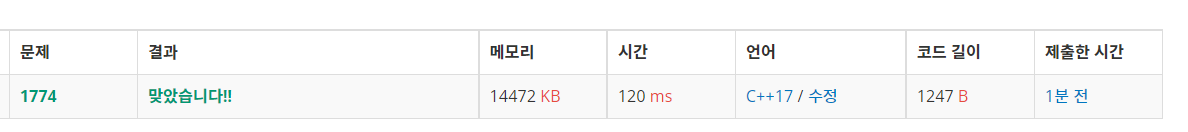
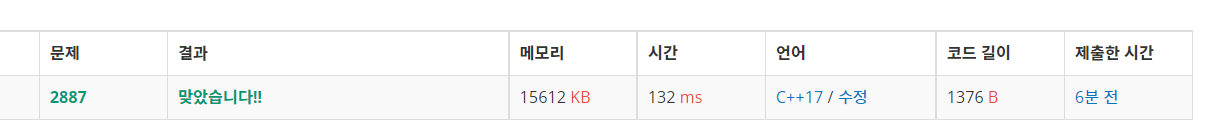
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/15683
15683번: 감시
스타트링크의 사무실은 1×1크기의 정사각형으로 나누어져 있는 N×M 크기의 직사각형으로 나타낼 수 있다. 사무실에는 총 K개의 CCTV가 설치되어져 있는데, CCTV는 5가지 종류가 있다. 각 CCTV가 감
www.acmicpc.net
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m, arr[9][9], ans = INT_MAX;
vector<pair<int, int> > cctv;
void up(int arr[][9], int x, int y) {
for (int i = x - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (arr[i][y] == 0) {
arr[i][y] = -1;
}
else if (arr[i][y] == 6) {
break;
}
}
}
void down(int arr[][9], int x, int y) {
for (int i = x + 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i][y] == 0) {
arr[i][y] = -1;
}
else if (arr[i][y] == 6) {
break;
}
}
}
void Left(int arr[][9], int x, int y) {
for (int i = y - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (arr[x][i] == 0) {
arr[x][i] = -1;
}
else if (arr[x][i] == 6) {
break;
}
}
}
void Right(int arr[][9], int x, int y) {
for (int i = y + 1; i < m; i++) {
if (arr[x][i] == 0) {
arr[x][i] = -1;
}
else if (arr[x][i] == 6) {
break;
}
}
}
void arr_init(int tmp[][9], int arr[][9]) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
tmp[i][j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
}
void DFS(int arr[][9], int L) {
int tmp[9][9];
arr_init(tmp, arr);
if (L == cctv.size()) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
ans = min(cnt, ans);
return;
}
else {
int x = cctv[L].first;
int y = cctv[L].second;
if (arr[x][y] == 1) {
up(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
down(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
Left(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
}
else if (arr[x][y] == 2) {
up(tmp, x, y);
down(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
Left(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
}
else if (arr[x][y] == 3) {
up(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
up(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
down(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
down(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
}
else if (arr[x][y] == 4) {
up(tmp, x, y);
down(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
up(tmp, x, y);
down(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
up(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
down(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
}
else if (arr[x][y] == 5) {
up(tmp, x, y);
down(tmp, x, y);
Left(tmp, x, y);
Right(tmp, x, y);
DFS(tmp, L + 1);
arr_init(tmp, arr);
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> arr[i][j];
if (arr[i][j] > 0 && arr[i][j] <= 5) {
cctv.push_back({ i,j });
}
}
}
DFS(arr, 0);
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
'Algorithm > problem' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 1699번: 제곱수의 합 (0) | 2022.02.21 |
|---|---|
| 백준 11003번 : 최솟값 찾기 C++ (0) | 2022.02.19 |
| 백준 12094번: 2048 (EASY) (0) | 2022.02.19 |
| 백준 12094번 : 2048 (Hard) C++ 문제풀이코드 (0) | 2022.02.19 |
| 백준 10423번: 전기가 부족해 - Prim MST 프림 최소스패닝트리 (0) | 2022.02.18 |